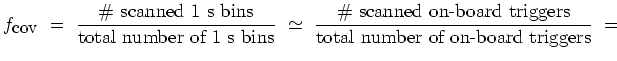 |
|||
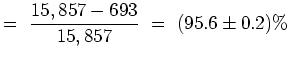 |
(37) |
To estimate the number
![]() of the on-board
triggers, corresponding to true GRBs, that could not have been
scanned by the off-line quest, the total number of GRBs automatically
detected on the archive data (
of the on-board
triggers, corresponding to true GRBs, that could not have been
scanned by the off-line quest, the total number of GRBs automatically
detected on the archive data (![]() , see table
, see table ![[*]](crossref.png) )
is required, and the result is expressed by the following
expression
)
is required, and the result is expressed by the following
expression ![[*]](crossref.png) :
:
![[*]](crossref.png) it comes out that the measured
number of bursts automatically detected by the off-line quest
has to be increased by its (
it comes out that the measured
number of bursts automatically detected by the off-line quest
has to be increased by its (
On the other side, since one the advantages of the early
SWTCs is that they can be applied also in these ``forbidden''
regions, the 10 GRBs recovered thanks to them
(table ![[*]](crossref.png) ) come from this
) come from this ![]() 40 missed GRBs.
Furthermore, the low efficiency of the early SWTCs
with respect to the late ones is apparent, as well: in fact,
from the rate of GRBs detected with the late SWTCs,
40 missed GRBs.
Furthermore, the low efficiency of the early SWTCs
with respect to the late ones is apparent, as well: in fact,
from the rate of GRBs detected with the late SWTCs, ![]() 40
GRBs are expected to be scanned by the only early SWTCs, while
the formers are able to catch only a quarter.
In conclusion, this clearly shows that the early SWTCs
sensitivity is significantly worse than for the late SWTCs,
in agreement with the belief that the formers have a better efficiency.
40
GRBs are expected to be scanned by the only early SWTCs, while
the formers are able to catch only a quarter.
In conclusion, this clearly shows that the early SWTCs
sensitivity is significantly worse than for the late SWTCs,
in agreement with the belief that the formers have a better efficiency.